Understanding the https://acortaz.eu/ipv4-e-ipv6-comparacion is essential as our digital landscape continues to grow and evolve. The internet’s increasing complexity, driven by the rise of connected devices, has made effective IP addressing more critical than ever. This guide will provide a comprehensive comparison between these two key protocols, highlighting their evolution, technical features, and the benefits they offer in the modern world. The focus keyword, https://acortaz.eu/ipv4-e-ipv6-comparacion, is integrated throughout the content to ensure optimized search engine visibility and enhance user engagement.
Introduction to IPv4 and IPv6
In today’s interconnected digital era, IP addresses serve as a vital component of online communication, enabling seamless interactions between devices. Whether browsing websites, sending emails, or accessing cloud services, IP addresses facilitate the transmission of data across networks. However, the underlying protocols governing these IP addresses—IPv4 and IPv6—are not widely understood by most users, despite their significant differences.
IPv4 (Internet Protocol version 4) is the original protocol that still supports the vast majority of the internet’s infrastructure today. However, its limited address capacity has led to the development and gradual adoption of IPv6 (Internet Protocol version 6). The newer version offers greater scalability and introduces several advanced features designed to meet the demands of the modern digital environment. To gain deeper insights into the distinctions between IPv4 and IPv6, explore https://acortaz.eu/ipv4-e-ipv6-comparacion.
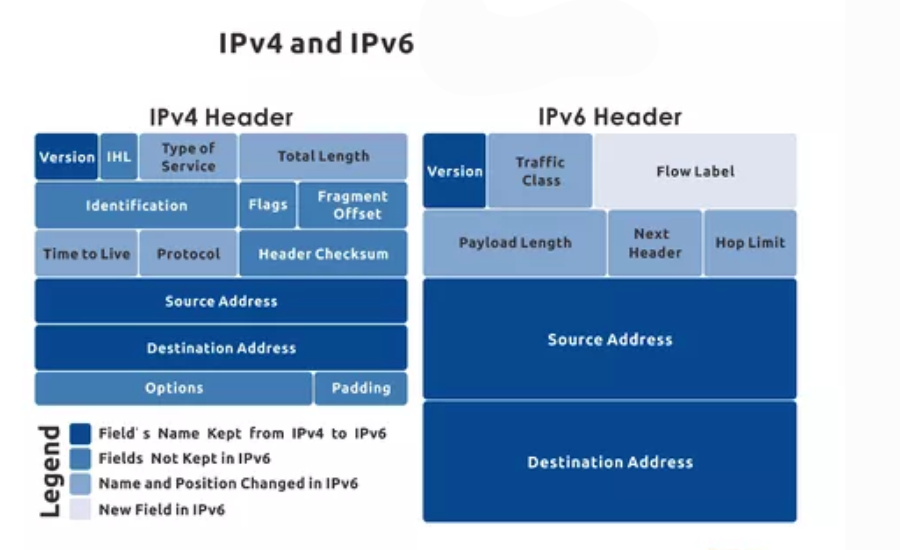
The Journey of IP Addressing: Transitioning from IPv4 to IPv6
Birth of IPv4 and the Early Internet
The concept of IP addressing dates back to the 1970s, with the creation of ARPANET, the precursor to today’s internet. IPv4 was introduced as the standard protocol for managing IP addresses, utilizing a 32-bit addressing system. This system was capable of generating around 4.3 billion unique addresses, which was more than adequate during the early days of the internet, when only a small number of devices were connected.
However, the explosive growth of the internet throughout the 1990s and 2000s—fueled by the proliferation of personal computers, smartphones, and IoT devices—quickly demonstrated the limitations of IPv4. The fear of running out of IP addresses led to the development of IPv6 in the late 1990s. By employing a 128-bit address space, IPv6 can support an astronomical number of unique IP addresses (approximately 340 undecillion), ensuring that the internet will be able to grow for decades, if not centuries, to come.
IPv6: A Solution for Future Internet Growth
The introduction of IPv6 was not simply a matter of adding more IP addresses. This newer protocol includes several enhancements that address the shortcomings of IPv4. For instance, IPv6 provides improved network security, more efficient routing, and easier configuration of devices. These features make it an essential protocol for modern and future networking. For more on the history and benefits of these two protocols, visit https://acortaz.eu/ipv4-e-ipv6-comparacion.
Key Differences Between IPv4 and IPv6
Address Structure and Capacity
One of the most noticeable differences between IPv4 and IPv6 lies in their address structure. IPv4 addresses are written as four sets of decimal numbers separated by periods (e.g., 192.168.1.1), whereas IPv6 addresses are much longer, using hexadecimal numbers separated by colons (e.g., 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334).
While IPv4’s 32-bit scheme provides approximately 4.3 billion addresses, IPv6’s 128-bit scheme offers an almost infinite number of unique addresses—about 340 undecillion. This vast difference ensures that IPv6 will be able to accommodate the massive expansion of internet-enabled devices, from smartphones and laptops to smart appliances and industrial sensors.
Configuration Methods: Manual vs. Auto-Configuration
Another key distinction between IPv4 and IPv6 is how they handle address configuration. IPv4 often relies on manual configuration or protocols like DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) to assign IP addresses. While this method works well for smaller networks, it can become cumbersome in larger or more dynamic environments.
On the other hand, IPv6 introduces auto-configuration capabilities, allowing devices to generate their own IP addresses automatically upon connection to the network. This makes setting up new devices faster and more efficient, especially in large-scale networks where frequent configuration changes are required.
Enhanced Security Features
Security is another area where IPv6 holds a distinct advantage. Unlike IPv4, which requires optional and manual configuration of security protocols like IPsec (Internet Protocol Security), IPv6 has IPsec built into its framework. This integration ensures that security measures such as data encryption and integrity checks are more robust and easier to implement.
For an in-depth comparison of these differences, along with visual charts and explanations, visit https://acortaz.eu/ipv4-e-ipv6-comparacion.

The Advantages of IPv6 Over IPv4
Larger Address Space
One of the most significant advantages of IPv6 is its massive address space, which provides a virtually unlimited number of IP addresses. This is especially crucial as the number of connected devices continues to skyrocket. While IPv4 is restricted to 4.3 billion addresses, IPv6’s 128-bit addressing system accommodates an almost unfathomable number of unique identifiers.
Improved Routing Efficiency
IPv6 also offers improved routing efficiency, thanks to its hierarchical addressing system. This system simplifies packet processing by reducing the workload on routers, making data transmission faster and more efficient. In large networks, this can significantly reduce latency and improve overall network performance.
Built-In Auto-Configuration and Mobility
Another standout feature of IPv6 is its ability to auto-configure devices, streamlining network management and simplifying the addition of new devices. This is particularly beneficial for Internet of Things (IoT) applications, where thousands of devices may need to be added to a network quickly and without manual intervention. Additionally, IPv6 supports better mobility by enabling seamless handovers between different network environments, making it ideal for modern mobile communications.
For further details on the specific advantages of IPv6, visit https://acortaz.eu/ipv4-e-ipv6-comparacion.
Implementation and Adoption of IPv6
The Slow but Steady Shift to IPv6
The shift from IPv4 to IPv6 is gradual but essential to meet the demands of today’s internet. Many organizations have implemented dual-stack systems, allowing both IPv4 and IPv6 to operate simultaneously. This strategy ensures that legacy systems remain compatible while facilitating the transition to the new protocol.
Government Initiatives and Industry Adoption
Governments around the world are playing a significant role in promoting IPv6 adoption, with many mandating its implementation in public sector networks. In countries like China and India, where internet penetration is rapidly expanding, IPv6 has already been widely adopted.
However, some organizations have been slow to transition due to legacy systems that do not fully support IPv6. Despite these challenges, network providers are offering extensive resources to help businesses upgrade their infrastructure and enable IPv6 adoption.
To explore more about the current state of IPv6 implementation, visit https://acortaz.eu/ipv4-e-ipv6-comparacion.

Transitioning from IPv4 to IPv6: What You Need to Know
Addressing IPv4 Exhaustion
The exhaustion of IPv4 addresses has been a major driver of the shift to IPv6. As mentioned earlier, IPv4 can only support 4.3 billion unique addresses, which is insufficient to handle the explosion of connected devices. IPv6, with its vast address space, provides the scalability needed to support the growing digital ecosystem.
Challenges and Solutions in IPv6 Transition
Transitioning to IPv6 is not without challenges. Many businesses face the issue of legacy systems that are not IPv6-compatible. To address this, many organizations are using dual-stack systems, allowing IPv4 and IPv6 to coexist until a complete transition can be made.
For more insights into how businesses are navigating this transition, check out https://acortaz.eu/ipv4-e-ipv6-comparacion.
Common Misconceptions About IPv6
Myth 1: IPv6 is a Temporary Solution
A common misconception is that IPv6 is only a temporary fix to address the IPv4 address shortage. In reality, IPv6 was designed to be a long-term solution. Its 128-bit address space offers trillions of unique IP addresses, ensuring that the internet can grow exponentially without running into address exhaustion issues. Unlike IPv4, which had a more limited foresight regarding the expansion of the internet, IPv6 has been carefully engineered to meet the demands of the future internet, accommodating a wide range of devices including IoT (Internet of Things) technologies. It’s a sustainable protocol meant to last for decades or even longer, making it a permanent replacement rather than a short-term patch.
Myth 2: Transitioning to IPv6 is Expensive and Complex
Another common myth is that transitioning from IPv4 to IPv6 is prohibitively expensive and too complex for most organizations. While the transition does require some investment in time and resources, most modern devices and networks already support both IPv4 and IPv6 protocols. The use of dual-stack systems, where both protocols run concurrently, allows organizations to make the transition gradually without significant downtime or operational challenges. In fact, many businesses are finding that the benefits of IPv6, such as improved security, scalability, and network performance, far outweigh the initial costs of migration.
Myth 3: IPv6 is More Difficult to Manage Due to Its Larger Address Structure
It is often believed that IPv6, with its larger 128-bit address structure, is more difficult to manage compared to IPv4. While it’s true that IPv6 addresses are longer and appear more complex, once understood, its hierarchical addressing system actually simplifies network management, particularly for large networks with thousands of devices. IPv6 is designed to facilitate more efficient routing and auto-configuration, which makes it easier to manage and scale networks as needed. Additionally, many modern network management tools are optimized to handle IPv6, making the transition smoother than expected.
Myth 4: IPv6 Adoption is Not Necessary for Most Organizations
Some organizations believe that adopting IPv6 is unnecessary, especially if their current IPv4 infrastructure is still functioning well. However, as the number of connected devices continues to grow exponentially, IPv4 addresses are becoming increasingly scarce, leading to higher costs for acquiring new addresses. Moreover, many modern internet services, mobile networks, and ISPs (Internet Service Providers) are shifting toward IPv6 as the standard protocol. Delaying adoption may result in compatibility issues and missed opportunities for network optimization. IPv6 also offers inherent security features and future-proofing that make it a necessary upgrade for most organizations.
Myth 5: IPv6 Does Not Offer Any Significant Benefits Over IPv4
Another misconception is that IPv6 does not provide significant advantages over IPv4. This is far from the truth. IPv6 offers built-in security features, such as IPsec (Internet Protocol Security), which provides robust encryption and authentication capabilities. It also allows for more efficient data routing and eliminates the need for Network Address Translation (NAT), which IPv4 relies on to extend its address space. IPv6 also supports auto-configuration, which simplifies the process of connecting new devices to the network. These enhancements make IPv6 far superior in terms of scalability, security, and network management.
FAQs About https://acortaz.eu/ipv4-e-ipv6-comparacion
Q: Why is IPv6 necessary when IPv4 is still functional?
A: IPv6 is necessary because IPv4’s address space is limited, and the rapid growth of internet-connected devices has exhausted the available IPv4 addresses. IPv6, with its vast address space, ensures continued internet expansion and supports future growth, especially with the rise of IoT devices.
Q: How long will the transition from IPv4 to IPv6 take?
A: The transition is gradual, and both protocols are expected to coexist for many years. The adoption rate varies by region and industry, with many organizations using dual-stack systems that support both IPv4 and IPv6.
Q: What are the main benefits of IPv6 over IPv4?
A: IPv6 offers several advantages, including a much larger address space, built-in security features like IPsec, more efficient routing, and auto-configuration capabilities. It also simplifies network management and supports future technologies.
Q: Is it expensive to transition from IPv4 to IPv6?
A: While the transition requires some investment in updating network infrastructure, the cost is often mitigated by using dual-stack systems that allow for a gradual shift. The long-term benefits of IPv6, such as improved scalability, security, and performance, outweigh the initial transition costs.
Q: Will IPv6 impact my current internet usage?
A: Most modern devices and networks already support IPv6, so most users won’t notice any difference. However, as IPv6 adoption increases, users may experience better performance, improved security, and more seamless connections as more services move to IPv6.
Q: Are there any security risks with IPv6?
A: IPv6 includes built-in security features such as IPsec, which can help enhance network security. However, like any protocol, it requires proper configuration and management to ensure secure usage.
Q: Do I need to manually configure devices for IPv6?
A: IPv6 supports auto-configuration, making it easier to connect devices to a network without manual setup. This is especially beneficial for large-scale networks and IoT devices.
Conclusion
The transition from https://acortaz.eu/ipv4-e-ipv6-comparacion is becoming increasingly critical as the digital landscape expands and the number of connected devices continues to grow. IPv4’s limited 32-bit address space is insufficient to support the vast range of internet-enabled devices, making IPv6, with its 128-bit address space, a necessary long-term solution. Beyond offering virtually unlimited IP addresses, IPv6 introduces key enhancements such as improved security, auto-configuration, and more efficient data routing. While the shift to IPv6 is gradual, often managed through dual-stack systems that accommodate both protocols, its adoption is inevitable due to the escalating demand for more IP addresses. IPv6’s advanced features, including built-in security, greater scalability, and future-proofing capabilities, make it indispensable for modern networks. As organizations worldwide embrace this new protocol, understanding the differences, benefits, and challenges of transitioning to IPv6 is essential for staying ahead in today’s digital era.
Read Next: www-durostech-com